Other Decision-making Approaches
THEE's Framework
THEE identifies seven discrete and incompatible approaches to as shown in the box.
| ● | |
| ● | |
| ● | ~R&T's Strategist |
| ● | |
| ● | |
| ● | ~R&T's Expert |
| ● | ~R&T's Achiever |
Opposing Demands on Leaders
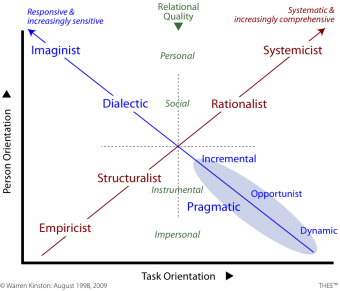
![]() Explanation of the TET (2x2 Table)
Explanation of the TET (2x2 Table)
Note that two very different sets of approaches lie along the diagonals. The two opposing sets are:
● systematic-controlling-comprehensive decision methods
● rapid-responsive-sensitive decision methods
Leadership occurs within a reality that is inherently messy, unknowable, unpredictable, and uncontrollable. So leaders need one decision approach from each diagonal to handle the two opposite types of work demand.
Pairing Decision Methods
Pairing them as shown allows the leader to maintain either the same degree of task orientation (vertical lines) or the same degree of person orientation (horizontal line).
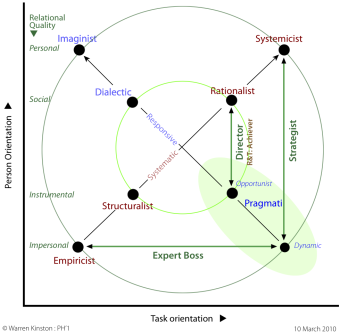
For any leader, one of the must be because it is easy to use and emphasizes .
► The combination with is what turns into (= R&T's Achievers)
► The same applies to the Expert leader: my preference is to label such a person as .
- Were any leadership categories related to these methods missed by R&T?
Last Updated: 23-Jan-2013